Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| TBL3 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | TBL3, SAZD, UTP13, transducin beta like 3 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 605915; MGI: 2384863; HomoloGene: 4711; GeneCards: TBL3; OMA:TBL3 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 16 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 16p13.3 | Start | 1,972,053 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 1,982,929 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 17 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 17|17 A3.3 | Start | 24,916,923 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 24,926,634 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - right testis
- left testis
- gastrocnemius muscle
- apex of heart
- muscle of thigh
- skin of leg
- skin of abdomen
- ectocervix
- mucosa of transverse colon
- right lobe of thyroid gland
|
| | Top expressed in | - spermatocyte
- epiblast
- spermatid
- morula
- embryo
- embryo
- ventricular zone
- Ileal epithelium
- maxillary prominence
- mandibular prominence
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 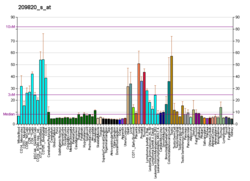 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- snoRNA binding
- RNA binding
| | Cellular component | - Pwp2p-containing subcomplex of 90S preribosome
- small-subunit processome
- nucleolus
- nucleus
- nucleoplasm
| | Biological process | - maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA)
- rRNA processing
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 16: 1.97 – 1.98 Mb | Chr 17: 24.92 – 24.93 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Transducin beta-like protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBL3 gene.[5][6]
The protein encoded by this gene has sequence similarity with members of the WD40 repeat-containing protein family. The WD40 group is a large family of proteins, which appear to have a regulatory function. It is believed that the WD40 repeats mediate protein-protein interactions and members of the family are involved in signal transduction, RNA processing, gene regulation, vesicular trafficking, cytoskeletal assembly and may play a role in the control of cytotypic differentiation. This gene has multiple polyadenylation sites. It might have multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants but the variants have not been fully described yet.[6]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000183751 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000040688 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Weinstat-Saslow DL, Germino GG, Somlo S, Reeders ST (Mar 1994). "A transducin-like gene maps to the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene region". Genomics. 18 (3): 709–11. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80380-5. PMID 8307582.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: TBL3 transducin (beta)-like 3".
Further reading
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. Bibcode:2005Natur.433...77A. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413. S2CID 4344740.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Scherl A, Couté Y, Déon C, et al. (2003). "Functional proteomic analysis of human nucleolus". Mol. Biol. Cell. 13 (11): 4100–9. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-05-0271. PMC 133617. PMID 12429849.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298. S2CID 14132033.

















